About Us
Vision
Mission
Values
Coverage Area
Iran at a Glance
Health Care in Iran
Farzan Clinical Research is the first Iranian Contract Research Organization (CRO). Our full-service CRO is now an important partner for many Universities, research centers, scientific societies as well as pharmaceutical and medical device industry.
After 10 years experience in providing medical research services as Farzan Science, Research & Technology Institute , Farzan Clinical Research was founded in Feb 2008 as the first Iranian registered CRO and now offering Clinical Trial Management, Clinical Trial Monitoring, Data Management, Biostatistics and Medical Writing services. Our focus is on innovative solutions that reduce cost and time for our customers.
Farzan Clinical Research is certified by Ministry of Health and Medical Education- Food and Drug Deputy- Islamic Republic of Iran.
vision
Our vision is to be a global partner in health research services and a pioneer contract research organization in the region to improve the human health.
Mission
Our mission is to improve both quality and quantity of clinical research by providing excellent research services for industry and investigators.
Values
• Innovation
• Excellence, Expertise, Experience
• Continuous Quality Improvement
• Timeliness, Responsiveness
• Research Bioethics
• Teamwork
Coverage Area
Farzan clinical research is a local contract research organization. We know the native investigators and the local regulatory process. Having a broad network of researchers in 17 major cities of the country, we are able to manage multicenter studies. This network makes it possible and facilitates to conduct national research projects.
Farzan Clinical Research Network
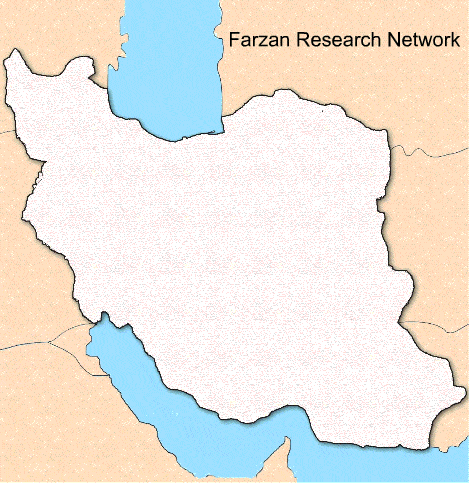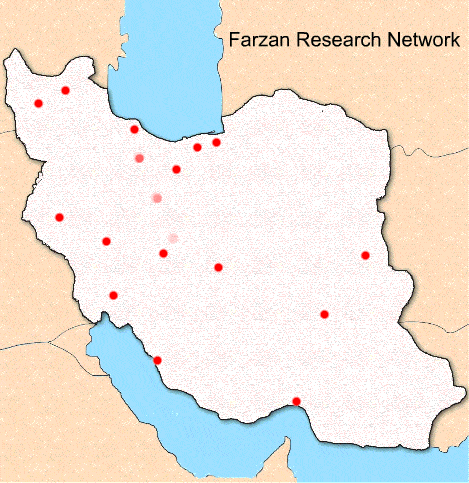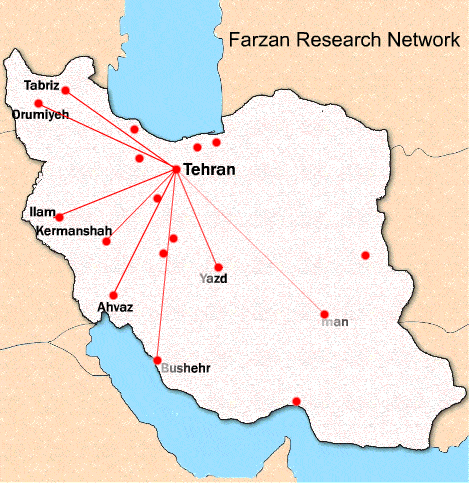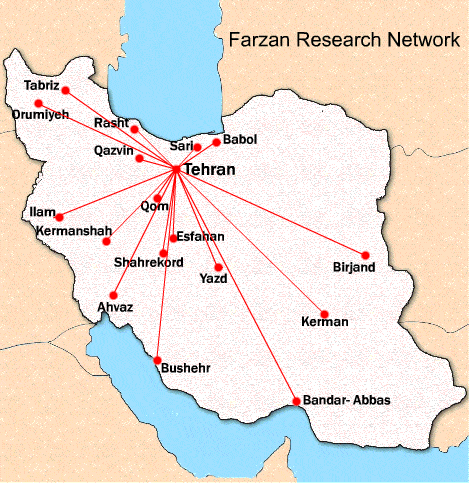
The cities of this network are as follow:
1. Tehran
2. Isfahan
3. Tabriz
4. Uromia
5. Ahwaz
6. Bandar-Abbas
7. Babol
8. Sari
9. Birjand
10. Rafsanjan
11. Yazd
12. Qazvin
13. Qom
14. Kerman
15. Kermanshah
16. Shahr-e-kord
17. Gonabad
Iran at a Glance
Iran/ Persia is a country in Central Eurasia. It is bounded by the Oman Sea and the Persian Gulf to the south and the Caspian Sea to its north. The 18th largest country in the world in terms of area at 1,648,195 km², Iran has a population of over seventy million.
Iran borders Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan to the north, Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and Turkey and Iraq to the west. Being a littoral state of the Caspian sea, an internal sea and condominium, Kazakhstan and Russia are Iran’s direct neighbors.
Iran is home to one of the world’s oldest continuous major civilizations, with historical and urban settlements dating back to 4000 BC.
Iran occupies an important position in international energy security and world economy as a result of its large reserves of petroleum and natural gas. The name Iran is a cognate of Aryan, and means “Land of the Aryans”.
Iran is a diverse country consisting of people of many religions and ethnic backgrounds cemented by the Persian culture.
Iran’s population increased dramatically during the latter half of the 20th century, reaching about 70 million by 2006. In recent years, however, Iran’s birth rate has dropped significantly. Currently the population is almost 75 million. Studies show that Iran’s rate of population growth will continue to slow until it stabilizes above 90 million by 2050. More than two-thirds of the population is under the age of 30, and the literacy rate is 82%.
Health Care in Iran
Health care in Iran and medical sector’s market value was almost US $24 billion in 2002 and is forecasted to rise to more than US $50 billion by 2013. With a population of almost 70 million, Iran is one of the most populous countries in the Middle East. The country faces the common problem of other young demographic nations in the region, which is keeping pace with growth of an already huge demand for various public services. Fifty percent of Iran’s population is currently under 20 years old. Soon they will be old enough to start new families, which will boost the population growth rate and subsequently the need for public health infrastructures and services.
The World Health Organization (WHO) in the last report on health systems ranks Iran’s performance on health level(DALE) 58th, and its overall performance 93rd among the world’s nations. The health status of Iranians has improved over the last two decades. Iran has been able to extend public health preventive services through the establishment of an extensive Primary Health Care Network. As a result child and maternal mortality rates have fallen significantly, and life expectancy at birth has risen remarkably. Infant (IMR) and under-five (U5MR) mortality rates have decreased to 26 and 31 per 1,000 live births, respectively in 2000, compared to an IMR of 122 per 1,000 and a U5MR of 191 per 1,000 in 1970. Immunization of children is accessible to most of the urban and rural population.
Today the largest healthcare delivery network is owned and run by the Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME) through its network of health establishments and medical schools in the country.
According to the last census that Statistical Centre of Iran undertook in 2003, Iran possesses 730 medical establishments (eg. hospitals, clinics) with a total of 110,797 beds, of which 488 (77,300 beds) are directly affiliated and run by the MOHME and 120 (11,301 beds) owned by the private sector and the rest belong to other organizations, such as the Social Security Organization of Iran (SSO). There were about seven nurses and 17 hospital beds per 10,000 populations.
Iran is in an epidemiologic transition and faces double burden of the diseases. New emerging threats should also be considered. The demographic and epidemiological transition underway will have a significant effect on the pattern of morbidity and mortality in the near and distance future, especially as it affects the emergence of chronic non-communicable diseases and the health problems of an aging population. In the early 2000s the main natural causes of death have been cardiovascular disease and cancer.
